Industrial robots enhance efficiency, improve precision, and reduce operational costs. Thanks to their advanced capabilities, these machines are transforming manufacturing processes by minimizing human error and accelerating production times. Among the available technologies are 3-axis, 4-axis, gantry, and vision robots, each with unique features and specific applications. Some robots are designed for standard work areas, such as 200×200 mm, 300×300 mm, or 400×400 mm. Choosing the correct work envelope is crucial, as it determines the robot’s ability to handle various part sizes and to integrate efficiently into the production line.
Understanding 3-axis and 4-axis robots
Industrial robots are often categorized by the number of movement axes they possess. The range of motion determines the complexity of tasks the robot can perform and influences its adaptability to different scenarios. Both 3-axis and 4-axis robots are widely used in industrial applications, each offering specific advantages depending on task requirements. Understanding the differences is essential for companies looking to integrate robotics into their production processes.
3-Axis robots
3-axis robots move in three principal directions: forward-backward, left-right, and up-down. These linear movements make them ideal for simple, repetitive tasks such as sorting or transferring items from one place to another. Their simplicity makes them suitable for applications where precision is important but movement complexity is minimal—such as on assembly lines where additional movements are unnecessary. Their relatively low cost and ease of maintenance also make them attractive for small businesses aiming to improve efficiency without investing in more complex technology.
Robots à 4 axes
By adding an additional rotational axis, 4-axis robots offer increased flexibility. This extra degree of rotation allows robots to handle objects with variable orientations—crucial in operations such as packaging, where precise positioning is required. They can rotate around a fixed point, enabling them to perform more complex tasks than 3-axis robots. 4-axis robots are commonly used in packaging, assembly, and other manufacturing processes where speed and precision are essential. Their ability to position objects at various angles also makes them useful in space-constrained environments by optimizing placement and workflow efficiency.
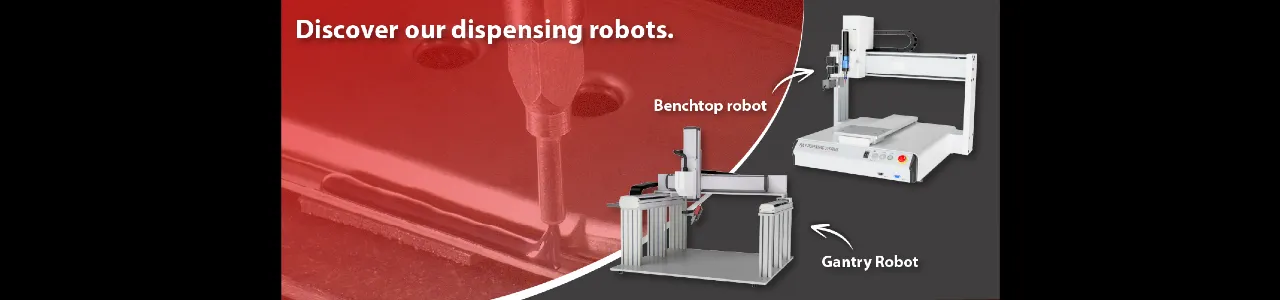
Gantry robots: choosing the right system
Gantry robots, also known as portal robots, are a specific type of system particularly suited to certain industrial applications. They offer unique features that make them more or less appropriate depending on the task at hand. Understanding their advantages can help you make the right choice for your business. By analyzing these distinctive capabilities, companies can align their production needs with the robot type that offers the best balance of cost and performance.
Gantry robots
Gantry robots move along fixed rails and are especially well-suited for fluid dispensing and high-precision tasks. Their portal-style configuration ensures stability and accuracy, making them ideal for operations requiring precise placement across large surfaces. These systems reduce the need for manual labor and increase the speed of dispensing processes. Their robustness and reliability make them a popular choice in industries requiring continuous operation over extended periods.
Integrating robot vision systems
Robot vision systems are revolutionizing how robots interact with their environment. By using cameras and sensors, robots can “see” and interpret their surroundings to perform tasks with enhanced precision. This visual analysis capability allows them to adapt dynamically to changes in their workspace, improving performance in complex scenarios. By integrating vision technology, companies can significantly increase the flexibility and accuracy of their robotic systems, minimizing errors and improving product quality.
Benefits of robot vision
- Enhanced flexibility: Vision systems allow robots to adjust to variations in their environment, such as changes in object size or orientation. This is particularly valuable on production lines where products may vary from batch to batch.
- Improved accuracy: Robots can modify their actions based on visual data, improving the accuracy of operations such as assembly and inspection. This leads to fewer human errors and higher final product quality.
- Process optimization: By analyzing visual data, robots can optimize production workflows, reducing downtime and errors. The ability to adjust operations in real time translates into increased productivity and better overall operational efficiency. Vision integration is especially valuable in industries with frequent production variations and high precision requirements. It also allows companies to respond quickly to market changes and maintain a competitive edge.
Industrial applications of robotics
Whether equipped with 3 or 4 axes, gantry systems, or vision capabilities, industrial robots are used across a wide range of sectors. Each robot type brings specific advantages that can be leveraged to boost productivity and enable innovation.
- Automotive: for assembly, welding, and painting. Robots enhance precision and speed while lowering labor costs and improving quality.
- Electronics: for component placement and PCB assembly. The speed and accuracy of robots ensure the high quality essential for delicate electronic parts.
- Aerospace: used for tasks such as drilling, riveting, and structural assembly. Their precision and ability to handle large parts improve build quality and shorten production times. Robots also enhance operator safety by taking on repetitive or hazardous tasks, such as composite handling or coating applications.
- Space Industry: in the space sector, robots assist in manufacturing complex components for satellites, rockets, and probes. They perform high-precision operations such as assembling miniature parts, non-destructive testing, and applying advanced materials. Automation enables the high reliability and quality required for space missions, while also optimizing costs and production lead times.
Conclusion: which robot for which application?
Choosing between a 3-axis, 4-axis, gantry robot, or vision-integrated system depends on several factors. Consider your application’s specific requirements, such as the level of precision, production speed, and payload capacity. A thorough evaluation of these criteria will help you select the most suitable robotic solution and fully capitalize on the benefits of automation.
Ultimately, adopting industrial robotics is a step toward advanced automation—boosting efficiency and competitiveness in a global marketplace. By investing in the right technology, companies can improve current operations and position themselves for future success in an ever-evolving industrial landscape.