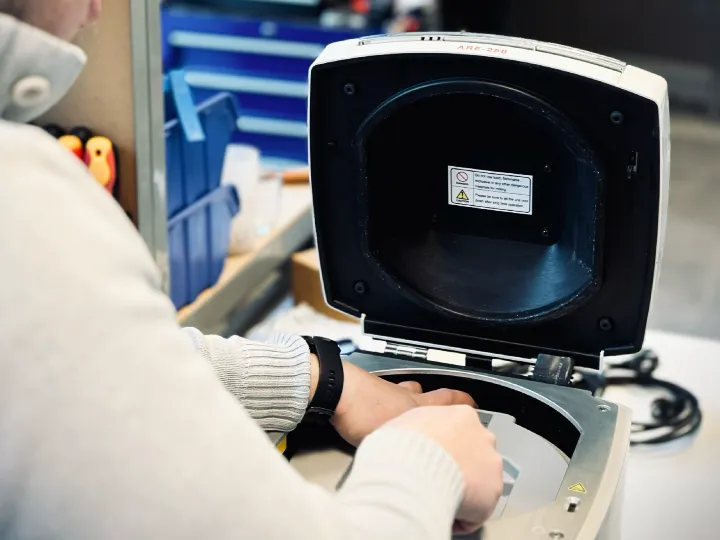




UV Drying
This process provides a fast and efficient method for creating durable bonds, coatings, or prints.
Using a UV drying system is essential to achieve the desired product performance and properties, ensuring your fluid reaches optimal strength and durability rapidly.
About UV Curing
What are the different curing techniques for your fluids?
Fluids can be cured using one of three methods:
- Ambient air humidity
- Thermosetting systems (e.g., ovens), where fluids harden under heat
- UV curing systems using wavelengths from 365nm to 405nm
How Does UV Curing Work?
You may be using an adhesive or ink that is a liquid material which, under normal conditions, remains soft and flexible until it has dried.
Ultraviolet (UV) light acts as a rapid trigger for chemical reactions within the product, allowing your adhesive or ink to transition from a liquid to a solid state.
As a result, the only way to activate this curing process is to expose the material to UV light, specifically within the wavelength range of 365nm to 405nm, enabling instant crosslinking and solidification.
Adhesives respond to different wavelengths due to their varying chemical compositions, which are characterized by different concentrations of oligomers or monomers. This variability necessitates the use of specific wavelengths for effective UV exposure.
The crosslinking of cyanoacrylates, also known as radical polymerization, is a chemical process in which cyanoacrylate molecules undergo polymerization reactions to form longer polymer chains.
When it comes to epoxy resins, the UV exposure initiates a cationic reaction, where epoxy polymerization is triggered by cation-based catalysts. To ensure effective crosslinking of epoxy resins, it is crucial to apply sufficient power over an extended period.
Our UV curing equipment is equipped with the most advanced LEDs on the market, making them ideally suited for epoxy UV adhesives and cationic-curing adhesives.
What Are the Technologies Used in Our UV Curing Systems?
The EXCELITAS UV curing systems, distributed by Poly Dispensing Systems, offer two distinct technologies: LED and mercury lamp.
Both technologies are perfectly suited to your specific needs depending on your application and usage. The choice between them will depend on the particular requirements of your process, such as:
- Wavelength precision
- Heat sensitivity of the material
- Usage constraints and technical criteria, among others
| LED | MERCURY | |
| Spectrum and Wavelength | Emission of a specific wavelength. | Emits a broad spectrum of wavelengths, adjustable with filters. |
| On/Off | Can be used immediately after switching on. | Requires a warm-up time before use. An immediate shutdown may affect the lamp’s lifespan. |
| Lifespan | More than 20,000 hours. Withstands frequent on/off cycles. | 2,000 hours with intensity decreasing over time. |
| Energy efficiency | More energy-efficient. | Generates more heat, making it less efficient. |
| Heat emission | Low heat, suitable for heat-sensitive materials. | Generates significant heat. |
| Maintenance | Calibration | Mercury bulb replacement and regular calibration required. |
What are the advantages of UV curing?
The drying of your products using a UV lamp offers numerous advantages across various sectors due to its unique characteristics. This crosslinking method is a preferred choice in applications where speed, precision, and enhanced material properties are key requirements.
Here are some noteworthy advantages of UV exposure when defining your specifications and setting up your production processes.
The physical properties of your fluids are optimized through this process. UV-cured materials frequently exhibit enhanced physical properties such as hardness, long-term durability, substrate adhesion, and chemical resistance, making them suitable for applications that require long-lasting performance and durability. The fast and controlled UV drying process contributes to uniform results, reducing defects and improving the overall quality of the products.
This improvement results in increased resistance, making the material more difficult to break, deform, or separate such as in the bonding of two parts. Additionally, enhanced hardness makes it more resistant to impacts and abrasions. On top of that, improved resistance to environmental factors allows the material to better withstand weather, chemicals, and heat.
UV exposure enables exceptionally fast curing, with product drying occurring in a matter of seconds to a few minutes, which significantly accelerates your production particularly critical in tight-deadline manufacturing processes. To further increase your production throughput efficiently, curing systems are compatible with automation systems such as Cartesian and gantry robots.
UV curing allows the UV lamp radiation to be focused on a precise area, which also helps reduce residual product loss. The instant curing characteristic reduces the spread or dripping of the fluid before it solidifies, since the reaction starts and ends almost instantly under UV light, thus offering better control over exposure time and, consequently, over the curing process.
A significant advantage is the reduced exposure to heat, which can be a critical condition when curing fluids on substrates with sensitive physical properties. Indeed, unlike certain traditional methods involving heat, UV curing is a cold process. This is particularly recommended for crosslinking operations on heat-sensitive materials, preventing any damage or deformation during the curing step.
The exposure step offers versatile adaptability of UV curing systems. UV drying can be applied to a wide range of materials, including inks, adhesives, coatings, and composites. Its versatility and compatibility with various substrates make it a preferred choice in multiple industries and application sectors.
Thanks to the short drying time, there is a noticeable gain in energy efficiency. UV curing systems, particularly LED systems, require relatively little energy compared to traditional methods like thermal drying, which can last several minutes or even hours. The initiation of the curing reaction by UV light limits energy consumption due to the short exposure period required to dry your product.
What are the applications where UV curing is used?
UV drying equipment can be used to meet specific industry standards and regulations.
It may be crucial to comply with certain requirements in the manufacturing specifications, taking into account specific physical characteristics that manufacturers must meet particularly in sectors such as aerospace, automotive, and electronics, where quality and performance standards are strict.
- MEDICAL: manufacturing of sterilized hypodermic needles, catheter production, manufacturing of infusion equipment, production of housings for automatic insulin dispensers
- AUTOMOTIVE: manufacturing of car headlights, drying process of varnishes applied to wooden steering wheel trims
- ELECTRONICS: production of fiber optic connectors, manufacturing of illuminated highway display panels, protection of electronic boards against moisture
- AERONAUTICS: manufacturing of turbine discs, protection of aluminum propellers
- MILITARY: production of night vision systems
- WATCHMAKING: watch decoration
- R&D: metrological control, creation of datasheets detailing the chemical reactions of UV products, including information such as the exact crosslinking time, for example.
Non-exhaustive list*
Looking for a high-performance UV curing solution ?
achievements
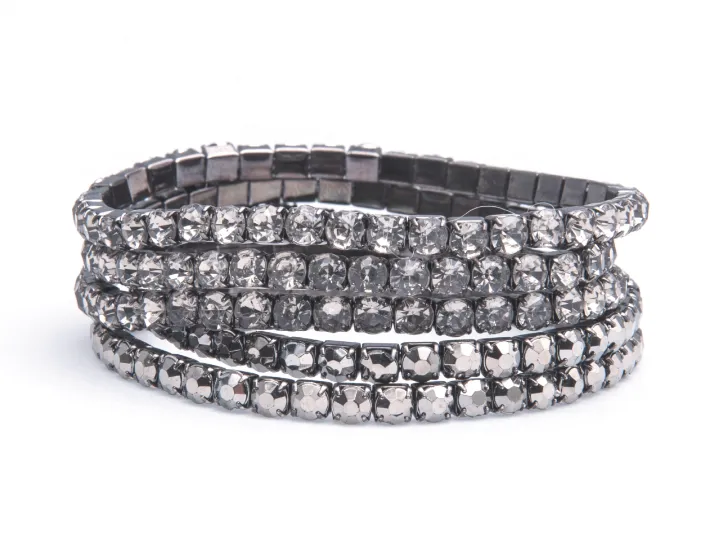


Jewelry: automation of two-component epoxy adhesive dispensing
Installation of an automated GRACO PR70 dispensing system...
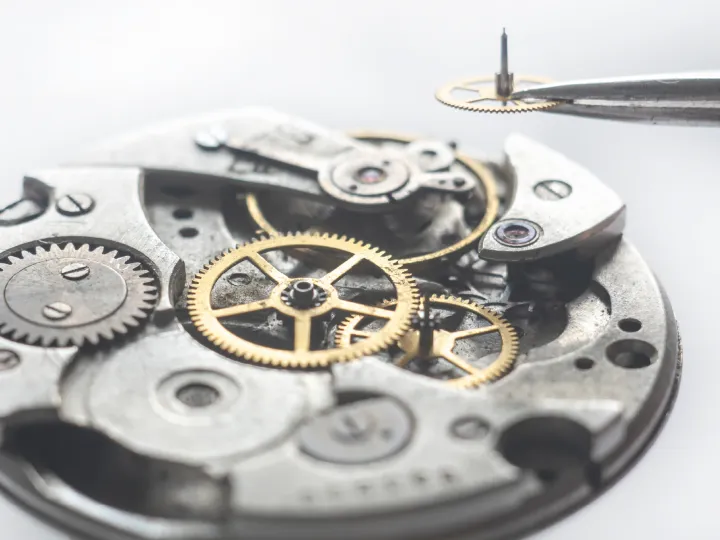


Watchmaking: automation of lubricating oil dispensing
Application of lubricating oil to eccentrics (small mecha...
Technical support
The technical team at Poly Dispensing Systems provides a comprehensive range of services. You can be assured that our experts are trained and specialized in operating all our equipment.

Study

Tailor-made offer

Trials
Delivery installation

Training
After Sales maintenance


